Small overlap front: driver-side
Rating applies to 2014-16 models built after October 2013
Tested vehicle: 2014 Mazda CX-5 Sport 4-door 4wd
The Mazda CX-5 was introduced in the 2013 model year. Beginning with 2014 models built after October 2013, the front and side airbag programming and the front structure were modified to improve occupant protection in small overlap frontal crashes. (Information about when a specific vehicle was manufactured is on the certification label typically affixed to the car on the driver door or adjacent B-pillar.)
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Chest | |
| Hip/thigh | |
| Lower leg/foot | |
| Driver restraints and dummy kinematics |
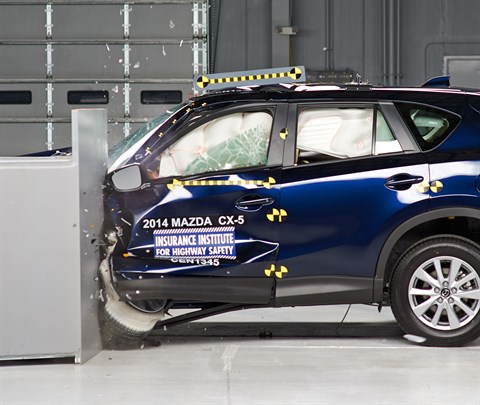

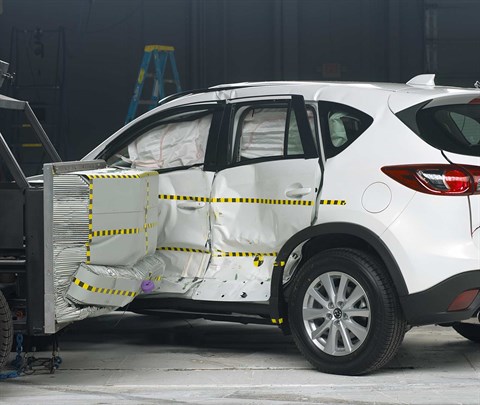
Action shot taken during the small overlap frontal crash test.
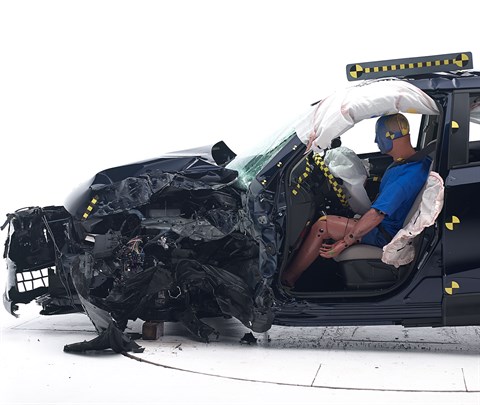

The dummy's position in relation to the door frame, steering wheel, and instrument panel after the crash test indicates that the driver's survival space was maintained reasonably well.
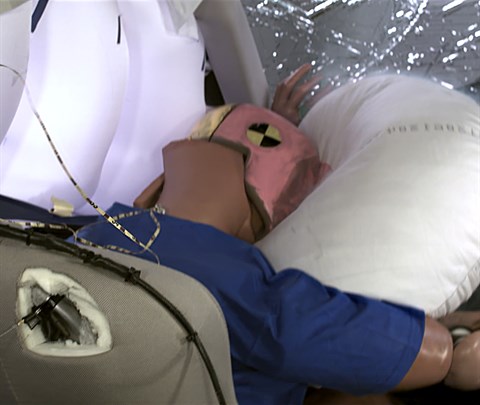
The frontal and side curtain airbags worked well together to keep the head from coming close to any stiff structure or outside objects that could cause injury.
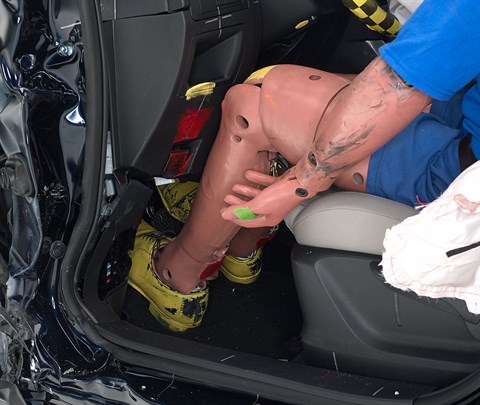

Intrusion into the driver's space was reasonably well controlled, and risk of injuries to the dummy's legs and feet was low.
Measures of occupant compartment intrusion on driver side
| Test ID | CEN1345 |
|---|---|
| Lower occupant compartment | |
| Lower hinge pillar max (cm) | 7 |
| Footrest (cm) | 7 |
| Left toepan (cm) | 5 |
| Brake pedal (cm) | 8 |
| Parking brake (cm) | |
| Rocker panel lateral average (cm) | 1 |
| Upper occupant compartment | |
| Steering column | 0 |
| Upper hinge pillar max (cm) | 8 |
| Upper dash (cm) | 7 |
| Lower instrument panel (cm) | 8 |
Driver injury measures
| Test ID | CEN1345 |
|---|---|
| Head | |
| HIC-15 | 181 |
| Peak gs at hard contact | no contact |
| Neck | |
| Tension (kN) | 1.4 |
| Extension bending moment (Nm) | 8 |
| Maximum Nij | 0.26 |
| Chest maximum compression (mm) | 24 |
| Femur (kN) | |
| Left | 1.4 |
| Right | 0.2 |
| Knee displacement (mm) | |
| Left | 3 |
| Right | 0 |
| Knee-thigh-hip injury risk (%) | |
| Left | 0 |
| Right | 0 |
| Maximum tibia index | |
| Left | 0.38 |
| Right | 0.48 |
| Tibia axial force (kN) | |
| Left | 1.3 |
| Right | 1.6 |
| Foot acceleration (g) | |
| Left | 52 |
| Right | 58 |
Moderate overlap front: original test
Rating applies to 2013-16 models
Tested vehicle: 2013 Mazda CX-5 Sport 4-door 4wd
The Mazda CX-5 was introduced in the 2013 model year.
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Chest | |
| Leg/foot, left | |
| Leg/foot, right | |
| Driver restraints and dummy kinematics |
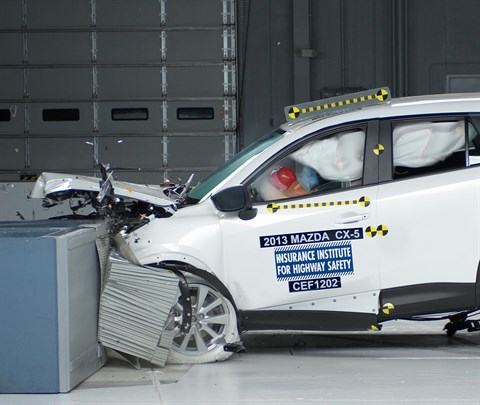

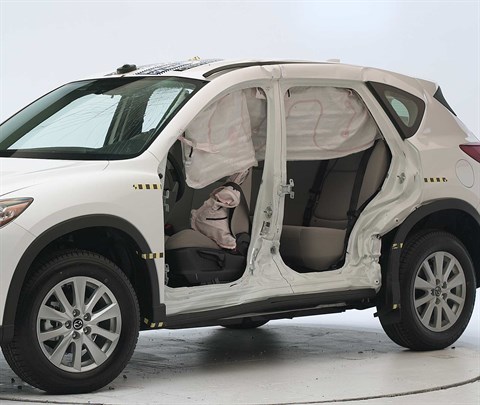
Action shot taken during the frontal offset crash test.
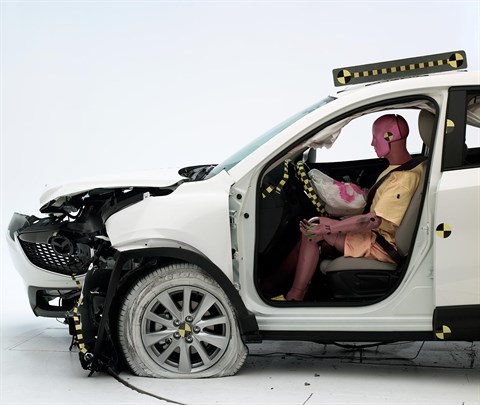

The dummy's position in relation to the steering wheel and instrument panel after the crash test indicates that the driver's survival space was maintained very well.
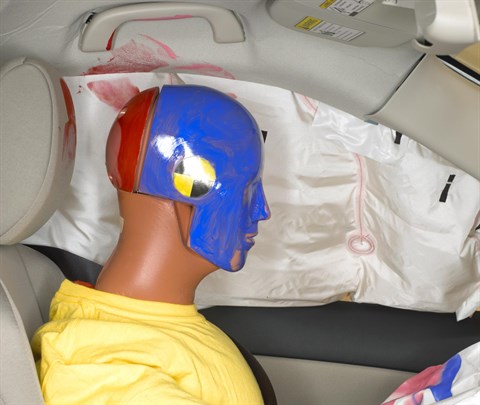

Smeared greasepaint indicates where the dummy's head contacted the side curtain airbag, headliner, grab handle, and head restraint during rebound.
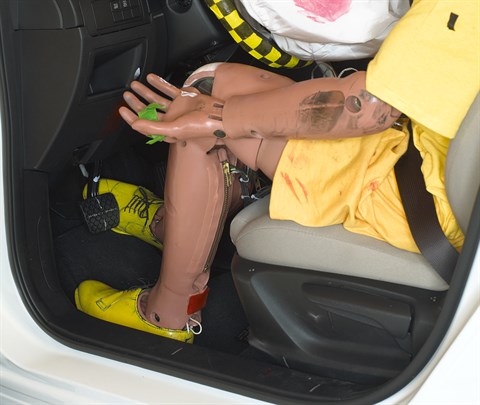

Intrusion into the driver's space was minimal, and all leg and foot injury measures were low.
Measures of occupant compartment intrusion on driver side
| Test ID | CEF1202 |
|---|---|
| Footwell intrusion | |
| Footrest (cm) | 3 |
| Left (cm) | 6 |
| Center (cm) | 8 |
| Right (cm) | 4 |
| Brake pedal (cm) | 2 |
| Instrument panel rearward movement | |
| Left (cm) | 0 |
| Right (cm) | -1 |
| Steering column movement | |
| Upward (cm) | -2 |
| Rearward (cm) | -4 |
| A-pillar rearward movement (cm) | 0 |
Driver injury measures
| Test ID | CEF1202 |
|---|---|
| Head | |
| HIC-15 | 325 |
| Peak gs at hard contact | 17 |
| Neck | |
| Tension (kN) | 1.0 |
| Extension bending moment (Nm) | 12 |
| Maximum Nij | 0.25 |
| Chest maximum compression (mm) | 27 |
| Legs | |
| Femur force - left (kN) | 0.2 |
| Femur force - right (kN) | 1.0 |
| Knee displacement - left (mm) | 0 |
| Knee displacement - right (mm) | 0 |
| Maximum tibia index - left | 0.21 |
| Maximum tibia index - right | 0.68 |
| Tibia axial force - left (kN) | 1.5 |
| Tibia axial force - right (kN) | 1.6 |
| Foot acceleration (g) | |
| Left | 45 |
| Right | 46 |
Side: original test
Rating applies to 2013-16 models
Tested vehicle: 2013 Mazda CX-5 Sport 4-door 4wd with standard front and rear head curtain airbags and standard front seat-mounted torso airbags
The Mazda CX-5 was introduced in the 2013 model year.
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Torso | |
| Pelvis/leg | |
| Driver head protection | |
| Rear passenger injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Torso | |
| Pelvis/leg | |
| Rear passenger head protection | |

View of the vehicle and barrier just after the crash test.

View of the vehicle after the crash with doors removed, showing the side airbags and damage to the occupant compartment.
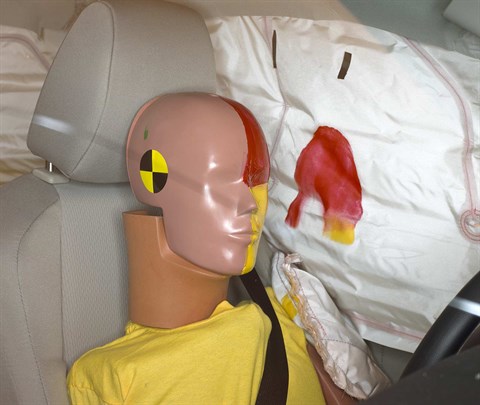

Smeared greasepaint shows where the driver dummy's head was protected from being hit by hard structures by the side curtain airbag.
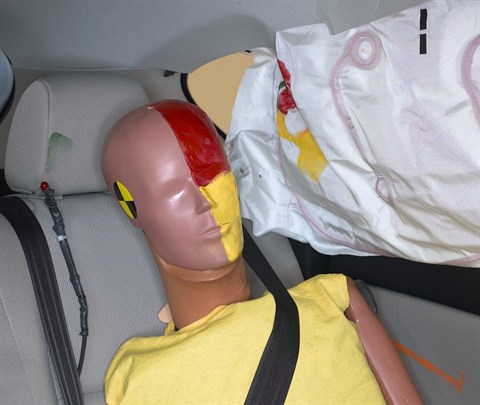

Smeared greasepaint shows where the rear passenger dummy’s head was protected by the side airbag.
Measures of occupant compartment intrusion on driver side
| Test ID | CES1202 |
|---|---|
| B-pillar to longitudinal centerline of driver's seat (cm) | -18.5 |
| Negative numbers indicate the amount by which the crush stopped short of the seat centerline. | |
Driver injury measures
| Test ID | CES1202 |
|---|---|
| Head HIC-15 | 188 |
| Neck | |
| Tension (kN) | 0.9 |
| Compression (kN) | 0.2 |
| Shoulder | |
| Lateral deflection (mm) | 30 |
| Lateral force (kN) | 1.3 |
| Torso | |
| Maximum deflection (mm) | 20 |
| Average deflection (mm) | 18 |
| Maximum deflection rate (m/s) | 2.89 |
| Maximum viscous criterion (m/s) | 0.18 |
| Pelvis | |
| Iliac force (kN) | 1.7 |
| Acetabulum force (kN) | 1.5 |
| Combined force (kN) | 3.1 |
| Left femur | |
| L-M force (kN) | 1.3 |
| L-M moment (Nm) | 148 |
| A-P moment (Nm) | 46 |
Passenger injury measures
| Test ID | CES1202 |
|---|---|
| Head HIC-15 | 103 |
| Neck | |
| Tension (kN) | 0.2 |
| Compression (kN) | 0.7 |
| Shoulder | |
| Lateral deflection (mm) | 28 |
| Lateral force (kN) | 1.6 |
| Torso | |
| Maximum deflection (mm) | 23 |
| Average deflection (mm) | 16 |
| Maximum deflection rate (m/s) | 2.26 |
| Maximum viscous criterion (m/s) | 0.20 |
| Pelvis | |
| Iliac force (kN) | 0.2 |
| Acetabulum force (kN) | 2.3 |
| Combined force (kN) | 2.3 |
| Left femur | |
| L-M force (kN) | 1.0 |
| L-M moment (Nm) | 84 |
| A-P moment (Nm) | -45 |
Roof strength
Rating applies to 2013-16 models
Tested vehicle: 2013 Mazda CX-5 Sport 4-door 4wd
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Curb weight | 3,330 lbs |
| Peak force | 18,209 lbs |
| Strength-to-weight ratio | 5.47 |
Head restraints & seats
Seat type: Manual cloth seats
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Dynamic rating | |
| Seat/head restraint geometry |
| Seat type | Manual cloth seats |
|---|---|
| Geometry | |
| Backset (mm) | 20 |
| Distance below top of head (mm) | -2 |
| Seat design parameters | |
| Pass/fail | Pass |
| Max T1 acceleration (g) | 11.1 |
| Head contact time (ms) | 54 |
| Force rating | 1 |
| Neck forces | |
| Max neck shear force (N) | 0 |
| Max neck tension (N) | 174 |
How the head restraint & seat test is conducted
Currently, IIHS tests apply only to front seats.
Front crash prevention: vehicle-to-vehicle
Child seat anchors
Rating applies to 2015-16 models
| Overall evaluation |
|
| Vehicle trim | Touring |
| Seat type | cloth |
This vehicle has 2 rear seating positions with complete child seat attachment (LATCH) hardware.
It has 1 additional seating position with a tether anchor and the ability to borrow lower anchors from the other seating positions.
Note: When anchors are borrowed, they aren't available to use in their designated positions.
| Overall evaluation |
|
| Vehicle trim | Touring |
| Seat type | cloth |
| G | Good |
| A | Acceptable |
| M | Marginal |
| P | Poor |
|
|
Seating positions that rely on borrowed lower anchors or have only a tether anchor available are not rated. |
|
thether anchor symbol
|
Tether anchor |
|
lower anchor symbol
|
Lower anchors |
| Lower anchor(s) can be borrowed from adjacent positions(s) | |
|
|
No hardware available |
Details by seating position
| 1 | |
|---|---|
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| too deep in seat | |
| not too much force needed to attach | |
| easy to maneuver around anchors | |
| 2 | |
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| no other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| Can be borrowed from 1 and 3 | |
| 3 | |
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| too deep in seat | |
| not too much force needed to attach | |
| easy to maneuver around anchors |
Seat position 21
| Lower anchor A | |
|---|---|
| Open access rated | No |
| Depth (cm) | 2-4 |
| Force (lbs) | 13 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 66 |
| Lower anchor B | |
| Open access rated | No |
| Depth (cm) | 4-6 |
| Force (lbs) | 16 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 55 |
| Tether anchor | |
| Location | Middle seatback |
| Confusing hardware present | Yes |
| Has contrasting label within 3 inches of tether anchor |
No |
Seat position 22
| Lower anchor A | |
|---|---|
| Lower latch is shared for this seat position | |
| Lower anchor B | |
| Lower latch is shared for this seat position | |
| Tether anchor | |
| Location | Middle seatback |
| Confusing hardware present | No |
| Has contrasting label within 3 inches of tether anchor |
No |
Seat position 23
| Lower anchor A | |
|---|---|
| Open access rated | No |
| Depth (cm) | 4-6 |
| Force (lbs) | 22 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 61 |
| Lower anchor B | |
| Open access rated | No |
| Depth (cm) | 2-4 |
| Force (lbs) | 18 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 67 |
| Tether anchor | |
| Location | Middle seatback |
| Confusing hardware present | Yes |
| Has contrasting label within 3 inches of tether anchor |
No |
